What Is Legal Contributory Negligence?

Introduction
In personal injury law, the actions of the injured party can sometimes reduce or even eliminate their right to recover damages. This concept is called contributory negligence, and it focuses on how a plaintiff’s own negligence may contribute to their injury.
Contributory Negligence Simple Definition
Contributory negligence is a legal defense that prevents a plaintiff from recovering damages if they are found to have contributed in any way to the accident or injury, even if the defendant was primarily at fault.
Real-Life Examples of Contributory Negligence
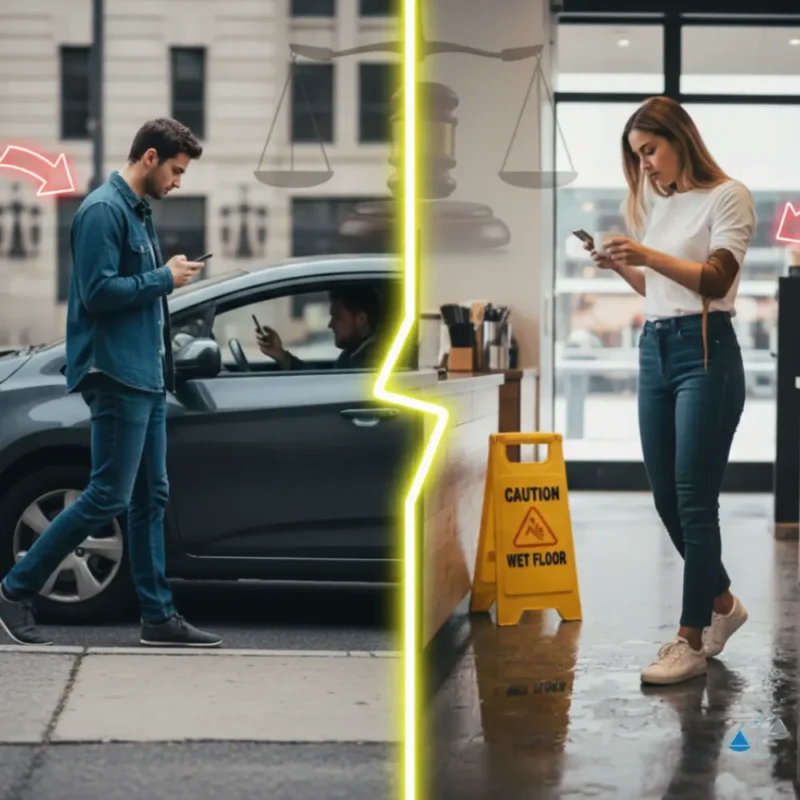
- Traffic accidents: A pedestrian crosses outside of a crosswalk and is hit by a speeding driver.
- Workplace safety: An employee ignores safety gear requirements and gets injured, reducing liability for the employer.
- Slip and fall: A customer ignores a “wet floor” sign and slips, limiting their ability to sue the store.
Importance of the Contributory Negligence
Contributory negligence is important because it highlights the responsibility individuals have for their own safety. While it can protect defendants from full liability, it has been criticized for being too harsh since even minor negligence by a plaintiff can bar recovery. Many jurisdictions have replaced it with comparative negligence rules.
Comparison: Contributory Negligence vs Comparative Negligence
Contributory Negligence: Any fault by the plaintiff completely bars recovery.
Comparative Negligence: Damages are reduced based on the plaintiff’s percentage of fault.
| Feature | Contributory Negligence | Comparative Negligence |
|---|---|---|
| Effect | Bars all recovery | Reduces recovery proportionally |
| Harshness | Very strict | More flexible |
| Example | Plaintiff 1% at fault → 0 recovery | Plaintiff 20% at fault → 80% recovery |
FAQ
1. What does contributory negligence mean in law?
It means the plaintiff’s own negligence contributed to their injury, potentially barring recovery.
2. Is contributory negligence still used today?
Yes, but only in a few jurisdictions, as most have adopted comparative negligence.
3. How is contributory negligence different from comparative negligence?
Contributory negligence bars recovery entirely, while comparative negligence reduces damages.
4. Can contributory negligence apply in traffic accidents?
Yes, if a pedestrian, cyclist, or driver’s actions contributed to the accident.
5. Why is contributory negligence controversial?
Because it can prevent injured parties from receiving compensation even for minor fault.
Closing
The doctrine of contributory negligence emphasizes personal responsibility in injury cases. Though considered strict, it remains an important legal principle in some jurisdictions, shaping how courts balance fault and liability.