What Is Negligence in Civil Law?
Negligence is a common legal concept in civil law, but it can be confusing for those without a legal background. This article explains negligence in simple terms, provides real-life examples, discusses its importance, and briefly compares it to similar concepts.
Simple Definition
Negligence in civil law means failing to take reasonable care, resulting in harm or loss to another person. If someone acts carelessly and their actions cause damage, they can be held legally responsible, even if they did not intend to cause harm.
Real-Life Examples
- Car Accident: A driver texts while driving and causes an accident. This is negligence because a careful driver would not use their phone behind the wheel.
- Slippery Floor: A grocery store fails to clean up a spilled liquid, and a customer slips and gets injured. The store’s failure to act carefully is considered negligence.
- Medical Error: A doctor forgets to check a patient’s allergy history and prescribes medicine that causes an allergic reaction. The doctor’s carelessness is negligence.
Why Is Negligence Important?
Negligence is central in civil law because it helps protect people from careless behavior. When individuals or companies are negligent, the law allows victims to seek compensation for their injuries or losses. This encourages everyone to act responsibly in daily life, at work, and in public places.
Comparison: Negligence vs. Intentional Harm
Negligence happens without intent to harm; it’s about carelessness. Intentional harm, however, means someone wanted to cause damage. For example, accidentally hitting someone with a car because you weren’t paying attention is negligence. Deliberately running someone over is intentional harm. The law treats these situations differently, with intentional acts often leading to harsher penalties.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the main elements of negligence?
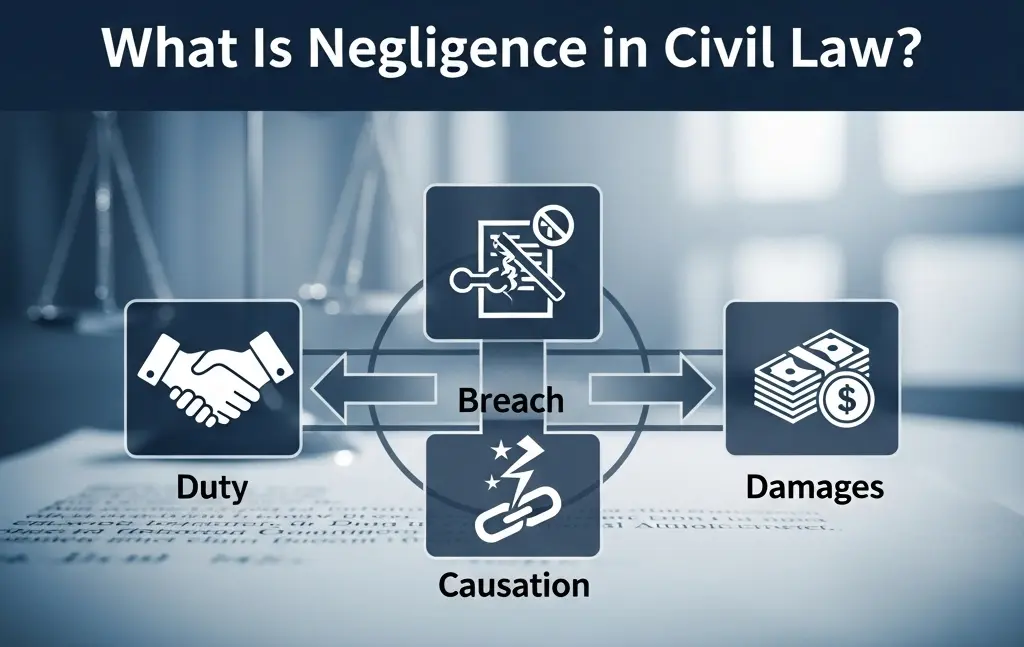
Negligence requires a duty of care, a breach of that duty, and harm resulting from that breach.
2. Can someone be sued for negligence without causing physical injury?
Yes, negligence can involve financial loss or emotional distress, not just physical injury.
3. Is negligence a crime?
Usually, negligence is handled in civil courts, not criminal courts, unless it leads to severe harm or death.
4. How do courts decide if someone was negligent?
Courts look at what a reasonable person would have done in the same situation.
5. Can both parties be negligent?
Yes, sometimes both the victim and the defendant share some responsibility. This is called “comparative negligence.”
Closing Thoughts
Understanding negligence in civil law helps people recognize their rights and responsibilities. Being careful protects not just you, but everyone around you.






