What Is a Legal Adhesion Contract?
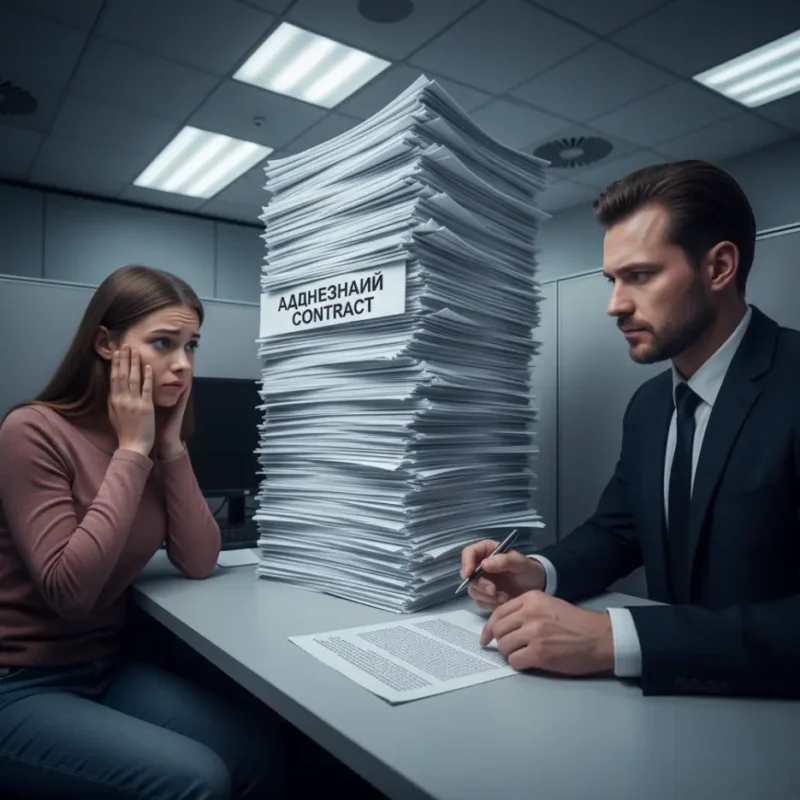

Not all contracts are negotiated equally. Sometimes one party has much stronger bargaining power and presents a “take it or leave it” agreement. This is called an adhesion contract, and it is common in consumer and business transactions.
Plain Definition
A legal adhesion contract is a standardized agreement drafted by one party, usually the one with greater power, leaving the other party little or no ability to negotiate terms.
Real-Life Examples of Adhesion Contracts
- Insurance policies: Customers accept pre-drafted terms without negotiation.
- Software licenses: Clicking “I agree” to terms of service agreements.
- Lease agreements: Landlords often present standard contracts tenants must accept as-is.
Importance of the Concept
Adhesion contracts are important because they streamline transactions and make business efficient, but they can also create unfairness. Courts may scrutinize such contracts to ensure terms are not overly one-sided or unconscionable.
Comparison: Adhesion Contract vs Negotiated Contract
Adhesion Contract: Standardized, non-negotiable terms.
Negotiated Contract: Terms discussed and agreed upon by both parties.
| Feature | Adhesion Contract | Negotiated Contract |
|---|---|---|
| Bargaining Power | One-sided | Balanced |
| Flexibility | Little to none | High |
| Common Usage | Consumer agreements | Business deals, partnerships |
FAQ
1. What does adhesion contract mean in law?
It is a standardized contract offered by the stronger party with little room for negotiation.
2. Are adhesion contracts enforceable?
Yes, but courts may strike down unfair or unconscionable clauses.
3. What are common examples of adhesion contracts?
Insurance policies, online terms of service, and rental agreements.
4. How are adhesion contracts different from negotiated contracts?
Adhesion contracts lack bargaining, while negotiated contracts involve mutual discussion.
5. Can consumers challenge adhesion contracts?
Yes, especially if terms are deceptive, oppressive, or unconscionable.
Closing
A legal adhesion contract reflects the imbalance of power in many everyday agreements. While they promote efficiency, courts remain cautious to ensure they do not unfairly disadvantage the weaker party.